Alcohol is a chemical substance and central nervous system (CNS) depressant drug. The type of alcohol contained in beer, wine and distilled spirits is ethanol. It contains calories but has little or no nutritional value.
For example:
- 150 calories in 12 ounces of regular beer
- 100 calories in 5 ounces of wine
- 100 calories in 1-1/2 ounces of 80-proof distilled spirits
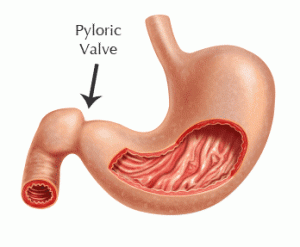
When alcohol is consumed, only a small percentage is absorbed through the mouth and stomach. At the base of the stomach is the pyloric valve. When food is present in the stomach, the valve remains shut, slowing down alcohol absorption until the food is digested. Without food, the pyloric valve is open which causes the alcohol to be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream through the lining of the small intestine then circulated throughout the body.
A link to continue to the next page will appear here when this time has elapsed.